Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete. The creep of concrete, which originates from the calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H) in the hardened Portland cement paste (which is the binder of mineral aggregates), is fundamentally different from the creep of metals and polymers. Unlike the creep of metals, it occurs at all stress levels and, within the service stress range, is linearly dependent on the stress if the pore water content is constant. Unlike the creep of polymers and metals, it exhibits multi-months aging, caused by chemical hardening due to hydration which stiffens the microstructure, and multi-year aging, caused by long-term relaxation of self-equilibrated micro-stresses in the nano-porous microstructure of the C-S-H. If concrete is fully dried, it does not creep, but it is next to impossible to dry concrete fully without severe cracking.
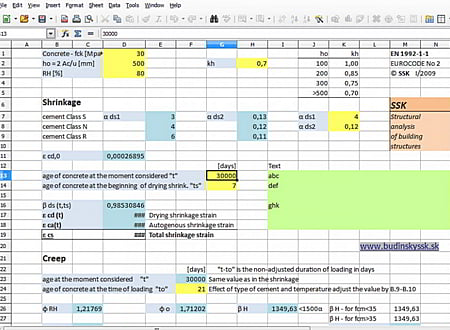
Creep
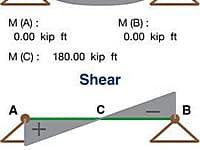
Creep is the gradual increase in a strain of a structural member which is subjected to certain loading over a period of time. When the concrete is loaded in compression, an elastic strain develops as shown in figure A. If this load remains on the member, creep strain developed with time.The main factors affecting creep strain are the concrete strength and mixture, the type of aggregate, curing, the relative humidity and the duration of the sustained loading.
Shrinkage
Shrinkage is the contraction that occurs in concrete when it dries and hardens due to moisture content evaporation. The amount of shrinkage increases with time as shown in figure B. The aggregate contents present in concrete are the most important factors influencing shrinkage. This is because the larger the aggregate, the lower is the shrinkage and the higher is the aggregate content, the lower the water-cement ratio and workability are. A decrease in ambient humidity also increases shrinkage.
* Creep and Shrinkage download link provides freeware version of the software.
Resultant of General Force System
The program is based on general principle of static equilibrium of forces in a plane.
Statics is a must have mobile software for every engineer (in particular civil or building), architect, Statics and Building science student.
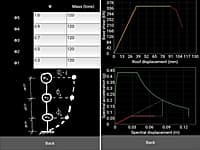
The app is useful for analyzing the results of a nonlinear static analysis (pushover analysis) based on Eurocode 8, N2 method.
Wind Analysis For Buildings In Accordances With Eurocode 1
Zephyr is a tool to assist engineers deal with Wind analysis for buildings in accordances with Eurocode 1 part 1-4
Steel and Composite Joints Design in Accordance with Eurocode 3
COP is an innovative computer program for the design of joints in steel and composite structures.
Submit a review about Creep and Shrinkage software with your social media profile