EPANET is a public-domain, water distribution system modeling software package developed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) Water Supply and Water Resources Division. It performs extended-period simulation of hydraulic and water-quality behavior within pressurized pipe networks and is designed to be "a research tool that improves our understanding of the movement and fate of drinking-water constituents within distribution systems".
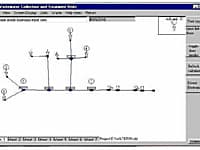
Pipe networks consist of pipes, nodes (junctions), pumps, valves, and storage tanks or reservoirs. EPANET tracks:
- the flow of water in each pipe,
- the pressure at each node,
- the height of the water in each tank, and
- the type of chemical concentration throughout the network during a simulation period,
- water age,
- source, and
- tracing.
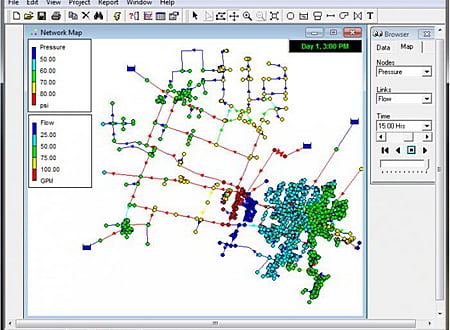
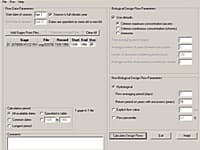
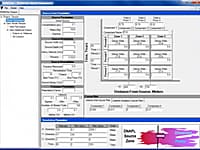
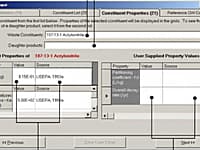
EPANET's Windows user interface provides a visual network editor that simplifies the process of building piping network models and editing their properties and data. EPANET provides an integrated computer environment for editing input data. Various data reporting and visualization tools are used to assist in interpreting the results of a network analysis. These include
- color-coded network maps,
- data tables,
- energy usage,
- reaction,
- calibration
- time series graphs,
- profile plots
- contour plots.
EPANET provides a fully equipped, extended-period hydraulic analysis package that can:
- Simulate systems of any size
- Compute friction head loss using the Hazen-Williams, the Darcy Weisbach, or the Chezy-Manning formula
- Include minor head losses for bends, fittings, etc.
- Model constant or variable speed pumps
- Compute pumping energy and cost
- Model various types of valves, including shutoff, check, pressure regulating, and flow control
- Account for any shape storage tanks (i. e. , surface area can vary with height)
- Consider multiple demand categories at nodes, each with its own pattern of time variation
- Model pressure-dependent flow issuing from sprinkler heads
- Base system operation on simple tank level, timer controls or complex rule-based controls
In addition, EPANET's water quality analyzer can:
- Model the movement of a non-reactive tracer material through the network over time
- Model the movement and fate of a reactive material as it grows (e. g. , a disinfection by-product) or decays (e. g. , chlorine residual) over time
- Model the age of water throughout a network
- Track the percent of flow from a given node reaching all other nodes over time
- Model reactions both in the bulk flow and at the pipe wall
- Allow growth or decay reactions to proceed up to a limiting concentration
- Employ global reaction rate coefficients that can be modified on a pipe-by-pipe basis
- Allow for time-varying concentration or mass inputs at any location in the network
- Model storage tanks as being complete mix, plug flow, or two-compartment reactors
* EPANET download link provides public domain version of the software.
Visualize, Reference, Analyze Water Distribution Networks
Online web application for visualizing, referencing, and analyzing water distribution models.
Water Quality Models and Tools
DFLOW 3. 1 is a Windows-based tool developed to estimate user selected design stream flows for low flow analysis and water quality standards.
WATER9, the wastewater treatment model, is a Windows based computer program and consists of analytical expressions for estimating air emissions of individual waste constituents in wastewater collection, storage, treatment, and disposal facilities; a datab
Remediation Evaluation Model for Chlorinated Solvents
REMChlor, or Remediation Evaluation Model for Chlorinated Solvents, is an analytical solution for simulating the transient effects of ground water source and plume remediation.
Industrial Waste Management Evaluation Model
The Industrial Waste Management Evaluation Model software is designed to assist you in determining the most appropriate waste management unit design to minimize or avoid adverse ground water impacts.
Submit a review about EPANET software with your social media profile

No comments yet. Be the first to comment.